The post How Can Hyaluronic Acid Combat Aging? appeared first on Stanford Chemicals.
]]>What is Hyaluronic Acid?
Hyaluronic acid (HA) is a naturally occurring substance in our bodies, primarily found in the skin, eyes, and connective tissues. Its main function is to retain moisture, keeping tissues well-lubricated and hydrated. With age, the natural levels of hyaluronic acid in the skin decline, contributing to dryness and the formation of wrinkles.

Moisture Retention and Hydration
One of the primary ways hyaluronic acid combats aging is through its exceptional ability to retain moisture. HA can hold up to 1,000 times its weight in water, creating a plump, hydrated appearance in the skin. This deep hydration helps to smooth out fine lines and wrinkles, making the skin look firmer and more supple.
Enhancing Skin Elasticity
As we age, the skin’s elasticity decreases, leading to sagging and the formation of wrinkles. Hyaluronic acid helps to improve skin elasticity by promoting the production of collagen and elastin—proteins that are essential for maintaining the skin’s structure and resilience. Increased collagen production also aids in repairing damaged skin cells, further enhancing skin firmness.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Inflammation can accelerate the aging process by breaking down collagen and elastin fibers. Hyaluronic acid possesses anti-inflammatory properties that help soothe irritated skin and reduce redness. By minimizing inflammation, HA protects the skin from environmental stressors that contribute to premature aging.
Promoting Skin Repair and Regeneration
Hyaluronic acid plays a crucial role in the skin’s repair mechanisms. It facilitates the migration of skin cells to areas of damage, promoting faster healing and regeneration. This not only helps in reducing the appearance of existing wrinkles but also prevents the formation of new ones by maintaining healthy skin cell turnover.
Improved Skin Barrier Function
A strong skin barrier is essential for protecting against external aggressors such as pollutants and UV rays, which can cause oxidative stress and accelerate aging. Hyaluronic acid strengthens the skin barrier by enhancing its hydration levels, making it more resilient and less prone to damage.
Versatile Application in Skincare
Hyaluronic acid is a versatile ingredient that can be incorporated into various skincare products, including serums, moisturizers, and even injectable treatments like dermal fillers. Topical applications provide surface hydration and elasticity, while injectable HA can offer more profound, volumizing effects by replenishing lost volume in deeper skin layers.
Conclusion
Hyaluronic acid is a powerful ally in the fight against aging, thanks to its unparalleled ability to retain moisture, enhance skin elasticity, reduce inflammation, and promote skin repair. Incorporating HA into your skincare routine can help maintain a youthful, radiant complexion and mitigate the visible signs of aging. Whether through topical products or professional treatments, hyaluronic acid offers a multifaceted approach to achieving and sustaining healthy, vibrant skin.
The post How Can Hyaluronic Acid Combat Aging? appeared first on Stanford Chemicals.
]]>The post Application of Micro Hyaluronic Acid as Carriers in Drug Delivery appeared first on Stanford Chemicals.
]]>The problem plaguing our customer
One of our customers faced a problem, macromolecule active ingredients (or at least 500KD) are historically difficult or impossible to deliver topically through tissue structures with the limitation of traditional methods.
The customer is a clinical-stage bio development company whose objective is to reduce society’s exposure to potentially harmful active agents by utilizing novel permeation technology to deliver active agents through tissue structures more efficiently.
“The topical delivery of large molecules through the skin, hair, eyes, mucosal surfaces, and bone are difficult using traditional hyaluronic acid.” said a medical director from one of our customers.
In the past, the most common form of hyaluronic acid in the pharmaceutical industry is high molecular weight HA, usually, more than 1800 K Da.
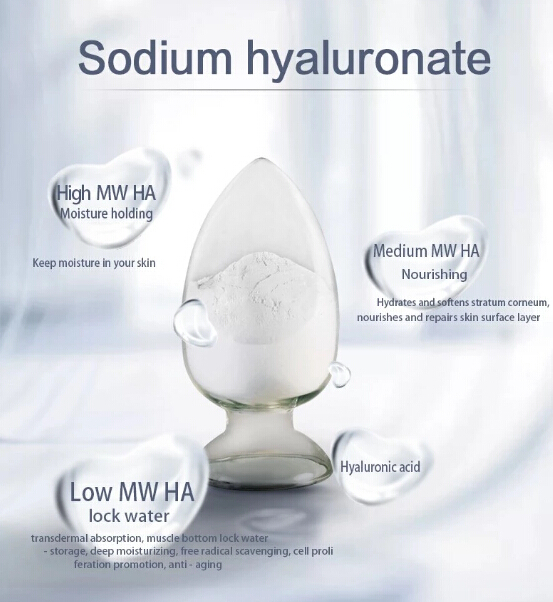
Low-molecular HA VS High-molecular HA
The difference between high-molecular hyaluronic acid (≥1,800 kDa) and low-molecular-weight HA (10 kDa ~1,000 kDa) is that the low-molecular-weight HA has been split into smaller fragments. The smaller fragments can no longer form a gel with water like the large molecules, but they can penetrate the skin much easier and have a better anti-irritant and regenerating effect once absorbed by the skin.
Why choose Stanford Chemicals?
In the past, the customer had purchased traditional mini HA (>10K Da) for its pharmaceutical delivery research. Over the years, Stanford Chemicals has developed HA with the low molecule that has stronger skin penetration, named micro hyaluronic acid (micro HA), which is a low molecular weight HA (<5K Da). It is even lower than the mini HA. The main functions of Micro HA are recovery and super moisturizing the tissues.
Stanford Chemical’s Micro-HA Super Active hyaluronic acid was used in Illustris molecule delivery technology to help facilitate a permeation process of the drugs in the human body. Micro hyaluronic acid as a drug carrier contributes to drug thickening, sustained release, transdermal absorption, and improved drug targeting.
By adopting the low molecular weight HA, the customer is able to provide a significant competitive advantage to molecule delivery, yielding enhanced safety and efficacy for patients.
Main Features of Micro HA
Since 5 kDa HA revealed a much more pronounced absorption activity through the skin than it could be observed for 10 kDa HA. Due to its micro size, micro-HA super active hyaluronic acid penetrates deep into the skin and other tissue structures easily, optimizing the absorption of compounds delivered through the skin, eyes, and mucosal. With the addition of micro HA, the cell proliferation rate of macromolecule active ingredients increased significantly; 0.125% micro HA can make the cell proliferation rate increase up to 94%.
There are 2 Benefits for Our customers
After utilizing our products Micro Hyaluronic Acid in its revolutionary delivery technology, they provide a significant competitive advantage with its novel approach to molecule delivery, yielding enhanced safety and efficacy for patients
“We are pleased to have used micro HA for Illustris’ innovative delivery technology,” said a technician from the pharmaceutical company, “We are eager to use micro HA and showcase its significant advantages over current drug delivery technology.”
Our customers benefited in the following ways:
Revolutionized HA solution for drug delivery system
The customer enables the delivery through tissue structures of macromolecule active ingredients (or at least 500KD) which are historically difficult or impossible to deliver topically and optimizes the delivery of active agents which previously permeated tissue structures inefficiently. It is easy for active ingredients to permeate the targeted site with Micro HA. Now, it enables the delivery of large molecules (up to 160KD) through tissue structures easily and optimizes the absorption of compounds typically delivered through skin, eyes, and mucosal surfaces.
Lower Cost
Stanford Chemicals (SCC) supplies high-purity micro HA at a very competitive price. Since the advanced specification of micro-HA, our customers can research its innovative delivery technology for pharmaceuticals easily. Therefore, this is a win-win result, it is also good news for the HA market. We are both happy with this transaction.
There are several benefits to using SCC micro HA throughout the pharmaceutical delivery process. For pharmaceutical companies with similar applications, our engineering team can provide a customized solution for your project. Feel free to contact us at [email protected].
The post Application of Micro Hyaluronic Acid as Carriers in Drug Delivery appeared first on Stanford Chemicals.
]]>The post Micro Hyaluronic Acid for Cosmetic Applications appeared first on Stanford Chemicals.
]]>The topical delivery of large molecules through skin, hair, eyes, mucosal surfaces and bone is difficult using high molecular weight hyaluronic acid.
In the past, the most common form of hyaluronic acid is high molecular weight, usually, more than 1800 K Da.
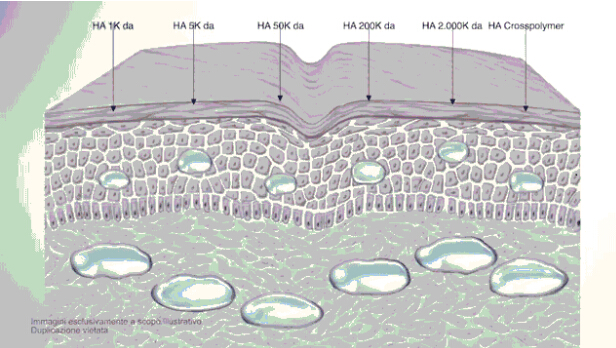
The difference between regular, high-molecular hyaluronic acid (HA) and low-molecular-weight HA is that the low-molecular-weight HA has been split into smaller fragments.
Thereby, these smaller fragments can no longer form a gel with water like the large molecules, but they can penetrate the skin much easier and have actually a better anti-irritant and regenerating effect once absorbed by the skin.
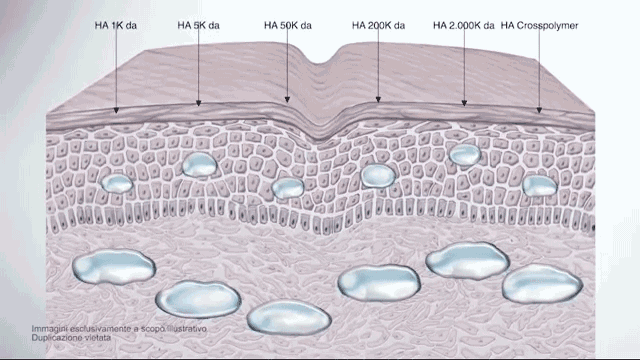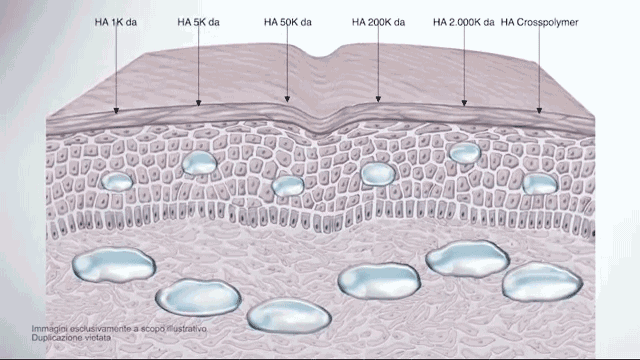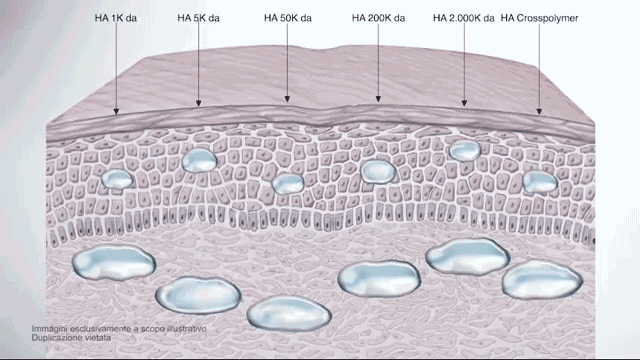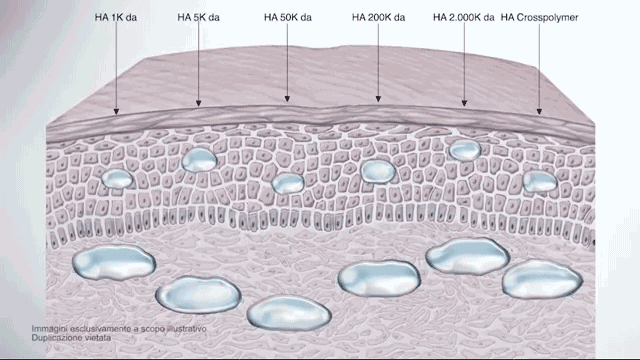
super active hyaluronic acid
Now, after several years, our new product Micro-HA Super Active hyaluronic acid was used in Illustris molecule delivery technology to help facilitate a permeation process.
Micro HA is a kind of very low molecular weight HA (<5K Da). It is even lower than mini HA (<10K Da).
Micro Hyaluronic Acid helps plump skin to improve volume and suppleness. Due to its micro size, it penetrates deep into the skin to infuse moisture below the surface, providing skin replenishment and moisturization from the inside out.
Micro-HA Super Active Hyaluronic Acid is a new low molecular weight active ingredient produced by a unique enzymatic degradation technology with superb biological activity. Micro-HA can quickly penetrate the epidermis and the dermis to scavenge free radicals, reduce inflammation factor activity, repair damaged cells, and protect the skin against inflammation and sensitivity caused by various stimuli.
In the past, the traditional industry or traditional HA-related products are more suitable for adults. However, after several years, we have designed a brand new product of HA. It is named micro HA. Micro HA is a kind of very low molecular weight HA (<5K Da). It is even lower than mini HA (<10K Da). The main functions of Micro HA are recovery and super moisturizing the tissues. It can increase the protection of baby care from daily life.
One of the examples from our customers
One of our regular customers was focused on personal care products. In the past, they sell more products for adults, especially for women. However, after utilizing products Micro HA in their new products, they obtained a lot. It is not only can enrich their product sorts, but also expand the market sales for their company. Since the advanced specification of micro-HA, they can search the new products for baby care. Therefore, this is a win-win result, it is also good news for the HA market. We are both happy about this transaction.
The post Micro Hyaluronic Acid for Cosmetic Applications appeared first on Stanford Chemicals.
]]>