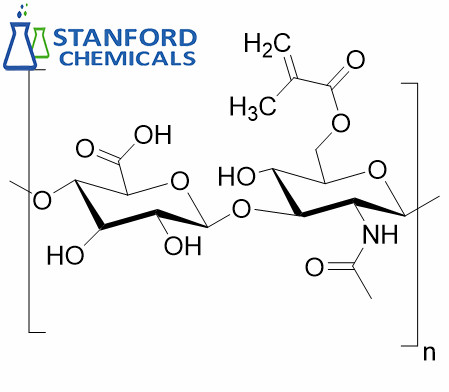
Introduction of Methacrylated Hyaluronic Acid (HAMA)
Hyaluronic acid is the most abundant glycosaminoglycan in the body being an important component of several tissues throughout the body. While it is abundant in extracellular matrices, hyaluronan also contributes to tissue hydrodynamics, movement, and proliferation of cells, and participates in a number of cell surface receptor interactions.
Methacrylated hyaluronic acid (HAMA) is for photocrosslinkable hydrogels. These hydrogels provide native-like 3D HA gels with the unique attributes to be prepared at various concentrations and photocrosslinked to provide various gel stiffness.
Methacrylated Hyaluronic Acid (HAMA), provides native-like 3D HA gels with the unique attributes to be prepared at various concentrations and photocrosslinked to provide various gel stiffnesses.

Specifications of Methacrylated Hyaluronic Acid (HAMA)
| Product Name |
Methacrylated Hyaluronic Acid (HAMA) |
| Molecular Weight |
100-150 kDa |
| Degree of Methacrylation |
45-65 % |
| Appearance |
Lyophilized powder |
| Storage |
-20°C |
| Shelf life |
Minimum of 6 months from date of receipt |
| Heavy metals |
≤ 20 ppm |
| Loss on drying |
≤ 10% |
Benefits of Methacrylated Hyaluronic Acid (HAMA)
Methacrylate hyaluronic acid (HAMA) is a modified form of hyaluronic acid (HA) with methacrylate groups introduced. This modification endows HA with enhanced functionalities. Here are the main benefits of MeHA:
1. Enhanced Mechanical Properties
Methacrylation significantly improves the mechanical strength and stability of HA. These enhanced mechanical properties allow MeHA to be used in applications that require higher mechanical stress, such as cartilage tissue engineering and other high-strength scaffold applications.
2. Adjustable Degradation Rate
The degradation rate of MeHA can be controlled by adjusting the content of methacrylate groups and the cross-linking density. This adjustability ensures suitable degradation speeds in different biological environments, meeting various medical and tissue engineering needs.
3. Biocompatibility and Biodegradability
MeHA retains the excellent biocompatibility and biodegradability of HA. It gradually degrades in the body and is safely absorbed and metabolized by biological systems, minimizing irritation and side effects.
4. Improved Adhesion Properties
Methacrylated HA exhibits enhanced cell adhesion properties. Its modified structure provides more binding sites, promoting cell adhesion and proliferation on the material surface. This is beneficial for cell culture and tissue construction in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.
5. Photocurable Properties
MeHA can be cross-linked using UV or visible light, enabling rapid in situ curing to form three-dimensional structures. This photocurable property offers unique advantages in minimally invasive surgery and tissue repair.
6. Versatility and Customizability
The chemical structure of HA becomes more versatile and customizable through methacrylation. Researchers can adjust its physical and chemical properties according to specific application needs, optimizing its performance in various biomedical applications.
Applications of Methacrylated HyaluronicAcid (HAMA)
▪ Because of its excellent mechanical properties and biocompatibility, HAMA is widely used in cartilage repair and regeneration.
▪ HAMA can be used as wound dressings, providing good structural support and a healing-promoting environment.
▪ HAMA is used as a skin filler and anti-aging treatment material, offering long-lasting effects and good tissue compatibility.
▪ Its adjustable degradation rate and good biocompatibility make it an ideal material for drug delivery systems.
▪ Used to form hydrogels for ex-vivo engineering of the autologous cartilage tissue or as a mesenchymal stem cell carrier in cartilage repair.
▪ Used to measure the effects of matrix stiffness on cell phenotype and function.
▪ Used for 3D bioprinting to create structures that promote osteogenic differentiation of MSC’s.
▪ The high tunability of hyaluronic acid methacrylate allows it to be mixed with, and reinforce other types of hydrogels (such as collagen, or gelatin methacrylate).
Reference:
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5717235/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5627486/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5541838/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5447944/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5615317/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21773726/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5460858/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5748291/