Sodium Hyaluronate (HA) is an important biomaterial in today's pharmaceutical and medical aesthetics industries. However, hyaluronic acid products of all grades marketed in the market vary significantly in application ranges, manufacturing methods, and quality requirements. Stanford Chemicals Company (SCC) offers medical-grade and injectable-grade sodium hyaluronate, two distinct systems of products with distinct needs.
Medical-Grade vs. Injectable-Grade Sodium Hyaluronate: Different Applications
Hyaluronic acid is typically classified into four grades based on its usage: food-grade, cosmetic-grade, medical-grade, and injectable-grade. Some brands are lumping medical-grade and injectable-grade into a single category. SCC particularly classifies medical-grade HA for non-injectable medical applications, such as surgical anti-adhesives barrier, wound dressings, and ophthalmic solutions. Medical-grade sodium hyaluronate is widely used in non-injectable medical fields:
- As a moisturizing agent in eye drops used in ophthalmic preparations to treat dry eye syndrome.
- As a wound-healing accelerator in topical creams and ointments, and also in ulcer and burn dressing applications.
- As a protective layer in medical-grade hyaluronic acid in nasal sprays to relieve dryness and inflammation.
- As a smart carrier for targeted and sustained drug release in drug delivery systems with hyaluronic acid of various molecular weights.
In addition, medicinal-grade HA is most commonly used in oral care products, gynecological products, and surgical anti-adhesion membranes.
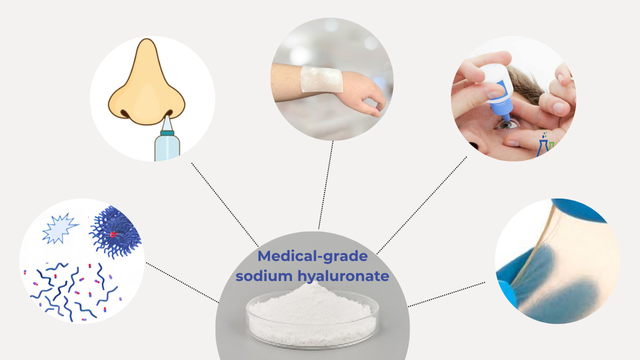
Medical-grade sodium hyaluronate applications Injectable-grade sodium hyaluronate, on the other hand, is specifically designed for direct injection into the human body:
- It is the main component of dermal fillers utilized in treatments like rhinoplasty, lip augmentation, and facial redefinition in medical aesthetics. Its rheological characteristics and stability in vivo are carefully controlled such that it is effective and degradable in a safe way.
- Injectable-grade hyaluronic acid is injected intra-articularly in orthopedics to treat osteoarthritis, providing joint lubrication, pain relief, and repair of cartilage.
- As an ophthalmic surgery viscoelastic device, injectable-grade hyaluronic acid of high purity maintains intraocular space and protects corneal endothelial cells in anterior chamber and vitreous surgery.
- It is used in anti-adhesive agents and promoters of wound healing that have to be in direct contact with sterile human tissue.
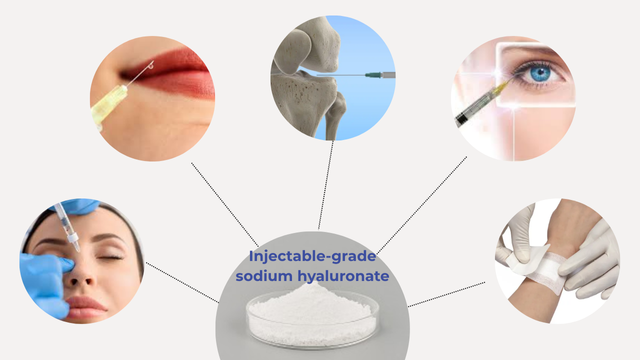
Injectable-grade sodium hyaluronate applications
Read more: 4 Grades of Hyaluronic Acid Raw Material Comparison
Injectable-Grade Sodium Hyaluronate Needs Stricter Requirements
Injectable-grade sodium hyaluronate is administered directly into the body and represents the highest level of quality control in the industry. These products must adhere to rigorous pharmacopoeial specifications, with each batch of production undergoing full physicochemical and biological testing.
- Molecular weight control: Injectable-grade sodium hyaluronate is typically restricted to a narrow range of 1,000–2,400 kDa to ensure consistent in vivo degradation rates and clinical performance.
- Endotoxin limits: Must be below 0.05 EU/mg—ten times more stringent than medical-grade standards (typically ≤0.5 EU/mg).
- Sterility assurance level (SAL): Requires 10^-6, i.e., not more than a single viable microorganism per million units, to provide absolute safety for direct human injection.
By comparison, medical-grade sodium hyaluronate follows relatively lenient pharmaceutical excipient standards:
- Adjustable molecular weight: Can be customized from low (50–100 kDa) to ultra-high (>2,500 kDa) based on application needs.
- Endotoxin level: Generally ≤0.5 EU/mg, which is sufficient for non-injectable use.
- Sterilization: Terminal sterilization is not a necessity; quality control places greater emphasis on chemical purity, protein residuals, and heavy metal content.
This differentiated standard makes medical-grade hyaluronic acid more cost-effective for large-scale pharmaceutical production. Hyaluronic acid injection into the joint
Conclusion & Selection Guidelines
Medical-grade and injectable-grade sodium hyaluronate represent two fundamentally distinct product standards and application philosophies. For healthcare professionals and product developers, the appropriate selection should be based on the following key considerations:
- The application method determines grade selection.
Any application requiring direct injection into the human body must use injectable-grade HA, including dermis, joint cavities, intraocular use, etc. For applications not involving direct contact with sterile tissues, medical-grade products may be considered.
- Risk-benefit balance.
While injectable-grade sodium hyaluronate carries higher costs, it provides essential safety assurance for high-risk applications. Of course, medical-grade products can offer more cost-effective solutions in appropriate application scenarios.
- Regulatory compliance.
Product registration categories and regional regulatory requirements directly influence HA grade selection. Target market regulations must be thoroughly understood in advance.
- Product performance requirements.
HA with different molecular weights exhibits distinct rheological properties and bioactivity. The optimal product specifications should be selected based on intended functional requirements. Stanford Chemicals Company (SCC) provides medical-grade and injectable-grade sodium hyaluronate products for comprehensive solutions tailored to diverse professional needs. Please refer to the sodium hyaluronate product COA certificates from SCC:
Send us an inquiry now.