Introduction
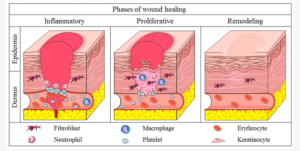
Wound healing is a complex biological process that involves a series of intricate cellular and molecular events aimed at restoring tissue integrity and function. In recent years, medical grade hyaluronic acid has emerged as a promising agent in promoting wound healing due to its unique properties and versatile applications.
This article explores the role of hyaluronic acid in wound healing, its mechanisms of action, and its potential benefits.
The Role of Hyaluronic Acid in Wound Healing
Hyaluronic acid is a naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan found in the extracellular matrix of tissues. It plays a critical role in tissue repair and regeneration. In wound healing, HA functions as a key component of the extracellular matrix. It promotes structural support, promotes cell migration, and modulates inflammatory responses.
Related reading: Medical-grade Sodium Hyaluronate Guide 2023: Functions & Applications
- Promotion of Cell Migration: Medical Grade Hyaluronic Acid facilitates the migration of various cell types involved in wound healing, such as fibroblasts, keratinocytes, and immune cells. By creating a scaffold for cell adhesion and migration, it helps to populate the wound bed with essential cells for tissue repair.
- Modulation of Inflammation: Medical Grade Hyaluronic Acid exhibits anti-inflammatory properties by interacting with immune cells and cytokines involved in the inflammatory phase of wound healing. By reducing inflammation and promoting a balanced immune response, it creates a favorable environment for healing.
- Enhancement of Tissue Regeneration: Through its ability to retain water and maintain tissue hydration, HA supports the formation of granulation tissue, angiogenesis, and collagen synthesis, essential processes for wound closure and scar formation.
Benefits of Medical Grade Hyaluronic Acid in Wound Healing
- Enhanced Wound Closure: Studies have shown that the application of hyaluronic acid to wounds can accelerate the closure of both acute and chronic wounds, such as surgical incisions, diabetic ulcers, and pressure sores.
- Reduced Scarring: By promoting organized collagen deposition and modulating the inflammatory response, HA may help reduce scar formation and improve the aesthetic outcome of healed wounds.
Related reading: Hyaluronic Acid: A Solution for Scar Reduction
- Moist Wound Healing: The hydrophilic nature of hyaluronic acid allows it to maintain a moist wound environment, which is conducive to cell migration, proliferation, and extracellular matrix deposition, leading to faster and more effective wound healing.
Clinical Evidence of Medical Grade Hyaluronic Acid
Medical Grade Hyaluronic Acid is available in various formulations, including gels, films, and dressings. They are designed for specific wound types and stages of healing. These products can be applied topically or in combination with other wound care modalities as well.
A review published in 2024 illustrated the effects of medical grade HA. This paper provides a review of HA use in wound healing, particularly focusing on challenging wounds to heal. It also explores HA's applications in ophthalmology and otorhinolaryngology. Additionally, it demonstrates HA's effectiveness as a versatile agent in medicine due to its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial properties. [1]
Such medical grade product is also combined with diverse substances in the process of wound healing. It was proved that the HA and iodine complex is effective in treating hard-to-heal wounds of various causes. [2] Clinical trials have also validated the efficacy of the medical grade hyaluronic acid and amino acids combination in treating various wounds. [3]
Future Directions
As research in wound healing continues to advance, the potential of medical grade hyaluronic acid in promoting tissue regeneration and improving wound outcomes remains a subject of ongoing investigation.
Further studies exploring novel delivery systems, combination therapies, and personalized approaches are likely to expand the therapeutic applications of hyaluronic acid in wound care. Here are some concise future directions:
- Advanced Delivery: Explore innovative delivery methods like hydrogels and nanoparticles.
- Combination Therapies: Combine HA with growth factors or stem cells for enhanced healing.
- Bioengineered Constructs: Develop scaffolds incorporating HA for tissue regeneration.
- Immunomodulation: Investigate HA's immunomodulatory effects for improved healing.
- Personalized Medicine: Tailor HA treatments based on patient characteristics for better outcomes.
- Clinical Trials: Conduct more trials to validate HA's efficacy and safety in wound care.
- Regenerative Medicine: Explore HA's potential in regenerating tissues and organs.
Conclusion
In summary, medical grade hyaluronic acid holds great promise in wound healing. It offers multiple benefits in promoting tissue repair, reducing scarring, and enhancing overall wound closure. By harnessing the regenerative properties of hyaluronic acid, clinicians can optimize wound care strategies and improve outcomes for patients with a variety of acute and chronic wounds.
Stanford Chemicals Company (SCC) is a leading wholesale supplier of pure organic HA in the USA. With extensive expertise, we offer a wide range of hyaluronic acid grades, including medical, cosmetic, and food grades. Our products encompass high, middle, and low molecular weight hyaluronic acid powders. Welcome to our website for HA products catering to various industries such as food supplements, cosmetics, eye drops, and pharmaceuticals.