What is Hyaluronic Acid Powder? Benefits and Usage
Hyaluronic acid powder, compared to liquid or gel forms, has a longer shelf life and higher stability, making it easier to store and transport.
What is Hyaluronic Acid
Hyaluronic acid (HA) is a natural glycosaminoglycan that occurs in connective tissue, skin, joint fluid, and the eye. HA has extremely high water-holding capabilities, allowing it to retain and bind an enormous amount of water. For this reason, hyaluronic acid occurs in cosmetics to provide moisture. In addition, HA serves lubricating and repairing functions and is used extensively in joint lubrication and cellular repair.
Benefits and Uses of Hyaluronic Acid for skin, eyes, and joints:
- Moisturizing: HA can hold between thousands of times its own weight in water, greatly enhancing skin hydration and erasing fine lines and wrinkles.
- Joint Lubrication: HA is utilized as a joint lubricant, reducing friction, joint pain, and improving joint function in patients with arthritis.
- Tissue Repair Stimulation: HA accelerates cell regeneration and tissue repair, wound healing, and scarring prevention.
- Ophthalmic Applications: In ophthalmic surgeries such as cataract surgery, HA is being used as a viscoelastic substance for supporting intraocular structures and protecting eye tissue.
What is Hyaluronic Acid Powder
Hyaluronic acid powder is the solid form of hyaluronic acid obtained through a drying process, typically supplied as a fine powder.
Fig 1. Pure Injection-Grade Sodium Hyaluronate Powder
How is Hyaluronic Acid Powder Produced in Industry
Hyaluronic acid has been classically obtained from animal tissues, specifically chicken combs or sturgeon bladders. With advancements in technology, biological fermentation, especially bacterial fermentation, has become the mainstream industrial method. This method is safer and more environmentally friendly compared to animal extraction.
Reference: How is Sodium Hyaluronate Powder Made
The majority of applications require the purity of sodium hyaluronate to be high, such as injection in medical or joint usage. Therefore, after extraction, hyaluronic acid undergoes a series of purification processes. Filtration and centrifugation are included to remove impurities and unwanted compounds.
The purified hyaluronic acid is typically concentrated by evaporation or other processes. The concentrated solution of HA can be further adjusted to the desired concentration.
To transform it into powder, the concentrated solution is dried. Spray drying and freeze-drying are commonly employed. Spray drying uses hot air to evaporate the liquid rapidly into powder, while freeze-drying evaporates the water at a low temperature to maintain the activity of the hyaluronic acid. The dried hyaluronic acid exists in the form of fine particles, which are sieved and filled into HA powder.
Advantages of Powder Form vs Other Forms
In addition to the powder form, hyaluronic acid is also available in liquid and gel forms. Compared to these, hyaluronic acid powder has a longer shelf life, higher stability, and is more convenient for storage and transportation.
Table 1. Powder Form vs Liquid Form vs Gel Form
| Feature | Powder Form | Liquid Form | Gel Form |
| Physical State | Dry powder | Liquid solution | Gel-like |
| Stability | Stable, long shelf life | Short shelf life, requires refrigeration | Short shelf life, needs airtight storage |
| Concentration | High concentration, adjustable when used | Lower concentration, fast effects | Moderate concentration, long-lasting hydration |
| Flexibility in Use | Can be mixed to create different concentrations and formulations | Pre-mixed, convenient but fixed concentration | Pre-mixed, provides steady hydration |
| Storage & Transport | Store at room temperature, avoid humidity | Store in a cool, dry place, avoid high heat or sunlight | Store in airtight containers, avoid exposure to air |
How to Use Hyaluronic Acid Powder
When using hyaluronic acid powder, solubility and concentration are key factors that directly impact the final result.
Solubility
Hyaluronic acid in a dry state cannot carry out its intended actions. HA needs to be dissolved in order to form a gel-like network where it exhibits moisturizing, lubricating, and other effects. The powder is to be dissolved in a proper amount of solvents to prepare the required concentration solution or gel. Dissolution method matters for achieving the desired effect. Inadequate dissolution may lead to undissolved particles, affecting both user experience and effectiveness.
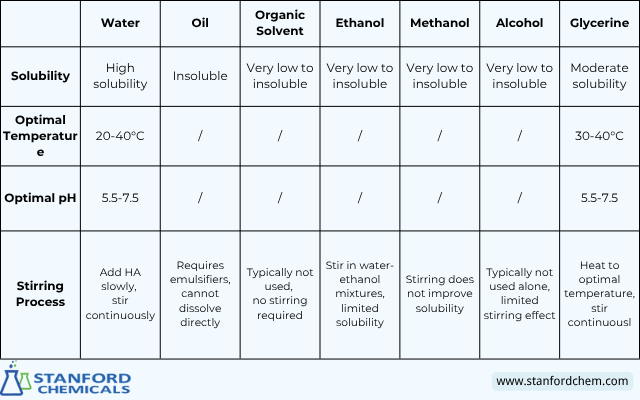
It should be noted that the solubility of HA varies in various solvents. HA is freely soluble in water and moderately soluble in glycerol, but has very poor solubility in oils, ethanol, methanol, and alcohol.
Table 2: Optimal Conditions for Dissolving Hyaluronic Acid in Different Solvents
In addition, temperature, pH, stirring, and time affect HA dissolution. For detailed instructions, please see my previous article: Solubility of Sodium Hyaluronate in Different Solvents and Its Influencing Factors
Tips for Dissolution:
- Use the solution as soon as possible after dissolving to avoid excessive exposure to air, which can cause bacterial growth or breakdown of active ingredients.
- Precipitation or clumping upon dissolution can be due to water that is too hot or of poor quality. Change the ratio and water temperature if this occurs.
Hyaluronic Acid Concentration
Concentration is also important when using hyaluronic acid (HA) powder. The concentration affects HA’s effectiveness, feel, how long it lasts, and where it can be used.
How HA Concentration Affects Effectiveness
Different HA concentrations work for different needs. Low concentrations (0.1%-0.5%) are good for daily skincare, while high concentrations (1%-2%) are used for anti-aging treatments or medical injections, like joint lubrication and eye treatments.
Controlling concentration helps HA work better. Higher concentrations give stronger hydration and repair but may feel sticky. But too high can cause discomfort. Too low may not provide enough moisture or repair.
How to Control Concentration
The key to controlling hyaluronic acid concentration is accurately calculating the ratio of powder to solvent. For example, to create a 1% hyaluronic acid solution, you would dissolve 1g of hyaluronic acid powder in 100ml of water. You can adjust the amount of powder based on your specific needs. For oral supplements, lower concentrations (0.1%-0.5%) are typically used, while medical treatments use higher concentrations (1%-2%) for more pronounced effects.
Conclusion
Hyaluronic acid powder offers versatility and stability, making it an excellent option for a variety of applications, from skincare to medical uses. By controlling solubility and concentration, you can tailor the powder to meet specific needs, ensuring effective and safe use.
Stanford Chemical Company (SCC) is a professional hyaluronic acid (HA) powder supplier.
SCC provides high-purity, high-quality, and safe sodium hyaluronate powder, including:
- Food-grade
- Cosmetic-grade
- Medical-grade
- Injection-grade
All SCC hyaluronic acid products are produced through bacterial fermentation, ensuring safety and reliability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Hyaluronic Acid Powder
1. What should I look for in hyaluronic acid powder for skincare products?
Choose powder that is over 95% pure. Make sure it comes in different molecular weights (50-2,000 kDa). Check that it meets ISO 22526 standards for microbes.
2. What’s the difference between medical and cosmetic grade hyaluronic acid powder?
Medical grade powder must pass endotoxin tests and have GMP certification. Cosmetic grade powder has stricter rules for heavy metals.
3. Can I use hyaluronic acid powder for injections?
Yes, but only if the powder has no endotoxins. It must also use approved sterilization methods.
4. How should I store large amounts of this hyaluronic acid powder?
Keep it in sealed containers. Store below 25°C with 60% humidity. For long storage, use nitrogen-filled packaging.
5. Does SCC provide product documents?
Yes. SCC gives you all needed papers. This includes quality certificates (COA), safety sheets (MSDS), and test reports.