Joint health is an important concern for many people, especially as they age. To manage joint pain and maintain flexibility, people often turn to supplements. Three popular choices are hyaluronic acid, glucosamine, and chondroitin. Each of these compounds offers unique benefits and mechanisms of action.
Understanding Joint Pain and Degeneration
Before diving into the specifics of each supplement, it’s essential to understand why joint pain occurs. Joints are complex structures where two bones meet, cushioned by cartilage and synovial fluid. Over time, wear and tear, injury, or conditions like osteoarthritis can lead to the breakdown of cartilage and a reduction in synovial fluid, causing pain, stiffness, and inflammation.
Hyaluronic Acid: The Lubricant
What Is Hyaluronic Acid?
Hyaluronic acid (HA) is a naturally occurring substance in the body's connective tissues, including the skin and cartilage. It's a major component of synovial fluid, which lubricates and cushions joints.
How Does Hyaluronic Acid Work?
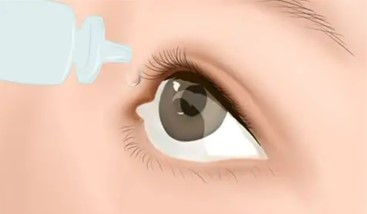
HA works primarily by retaining water, which helps to keep tissues well-lubricated and cushioned. In the joints, HA can absorb shocks and reduce friction between the bones. This property makes it a valuable component for maintaining joint health. In real life, there are two main ways to use hyaluronic acid for joint health. The most direct and effective method is to inject purified hyaluronic acid into the joint. This treatment usually lasts from six months to one year. Hyaluronic acid supplements for joints are easiest to take daily. After you take them by mouth, they are broken down and absorbed. Their fragments are then carried to the joint tissues. There, they help the body produce its own hyaluronic acid.
Reference: What Does Hyaluronic Acid Do For Joints?
Benefits of Hyaluronic Acid
- Lubrication: hyaluronic acid supplements may substitute for the synovial fluid within joints, which improves lubrication and reduces pain when moving.
- Inflammation Reduction: HA has anti-inflammatory activity that can decrease swelling and pain in the joints.
- Pain Relief: Patients generally note decreased pain and increased mobility with continued hyaluronic acid supplementation.
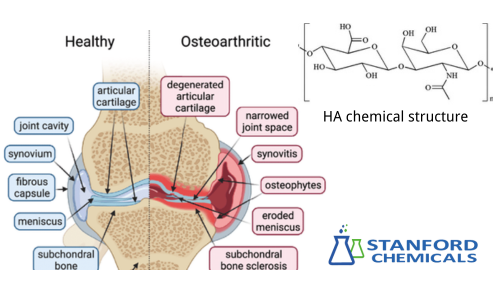
Fig 1. Hyaluronic acid for joints
Glucosamine: The Cartilage Builder
What Is Glucosamine?
Glucosamine is a naturally occurring amino sugar found in cartilage. It plays a crucial role in building and maintaining cartilage, the rubbery tissue that cushions bones at joints. Strong scientific evidence supports the use of glucosamine sulfate for the treatment of mild to moderate knee osteoarthritis. Studies show glucosamine is often taken with chondroitin sulfate for better results.
How Does Glucosamine Work?
Glucosamine supplements are believed to support cartilage regeneration and repair. They provide the building blocks needed for the synthesis of glycosaminoglycans, essential components of cartilage.
Benefits of Glucosamine
- Cartilage Repair: Glucosamine has been found to rebuild and repair deteriorated cartilage. It can reverse some of the damage that has accumulated as a result of wear and tear.
- Pain Relief: All studies suggest that pain resulting from arthropathy and function in patients with osteoarthritis can be reduced by glucosamine.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Glucosamine also possesses weak anti-inflammatory effects, which help in reducing swelling of joints and pain.
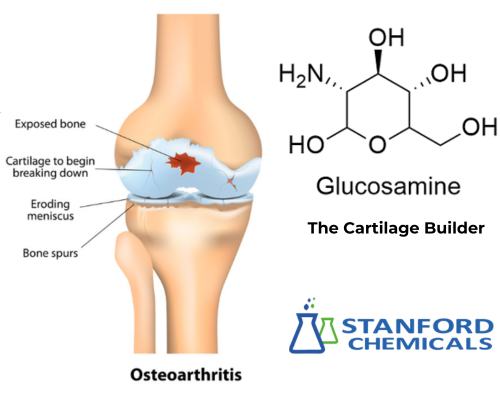
Fig 2. Glucosamine relieves osteoarthritis of the knee
Chondroitin: The Shock Absorber
What Is Chondroitin?
Chondroitin is another naturally occurring substance found in cartilage. It helps retain water in the cartilage, providing elasticity and resistance to compression.
How Does Chondroitin Work?
Chondroitin supplements are thought to enhance the shock-absorbing properties of cartilage. By retaining water, chondroitin helps maintain the structural integrity and elasticity of the cartilage. And with the help of it, cartilage is resistant to stress and damage.
Benefits of Chondroitin
- Cartilage Protection: Chondroitin can help protect existing cartilage from breakdown and may even stimulate the production of new cartilage.
- Pain Relief: Many users experience reduced arthrosis pain and improved joint function with chondroitin supplements.
- Reduced Inflammation: Chondroitin also has anti-inflammatory properties that can help alleviate joint swelling and discomfort.
Fig 3. Chondroitin helps joints absorb shock
Which Is Best for Arthrosis, Hyaluronic Acid, Glucosamine, or Chondroitin?
Choosing the best supplement for arthrosis depends on your specific needs and circumstances. Here’s a comparison to help you decide:
Hyaluronic Acid
Hyaluronic acid (HA) is highly effective for immediate relief from arthrosis pain and significantly improves arthrosis lubrication. This makes it ideal for individuals experiencing significant joint degeneration or those seeking a quick and effective solution to their joint discomfort. When the body’s natural levels of HA decrease due to age or joint disorders, supplementing with HA can restore joint fluidity, reduce pain, and enhance mobility. It is particularly beneficial for patients with advanced osteoarthritis, providing them with smoother joint movements and relief from chronic pain.
Glucosamine
Glucosamine is renowned for its long-term benefits in cartilage repair and maintenance. It is especially suitable for individuals with mild to moderate osteoarthritis who aim to prevent further cartilage degradation and support arthrosis health over time. By supplementing with glucosamine, you provide your body with the necessary building blocks to repair damaged cartilage, maintain its structural integrity, and possibly slow the progression of joint degeneration. This makes it a valuable option for individuals looking to manage their joint health proactively and sustain long-term joint function and comfort.
Chondroitin
Chondroitin is most suitable for patients with mild to moderate wear of articular cartilage, where the cartilage's morphology and structure remain largely intact. It is less effective for patients with severe or complete cartilage wear. By supplementing with chondroitin, individuals can support the resilience of their cartilage, reduce joint pain, and potentially slow the progression of cartilage degradation. This makes it an excellent choice for those in the early to mid stages of osteoarthritis or other arthrosis-related conditions.
| Supplement | Best For | Key Benefits | Ideal Candidates | Limitations |
| Hyaluronic Acid | Immediate pain relief & joint lubrication | - Improves joint fluidity - Reduces pain quickly - Enhances mobility | - Advanced osteoarthritis - Significant joint degeneration | Short-term effects, may need repeated use |
| Glucosamine | Long-term cartilage repair | - Supports cartilage regeneration - Maintains joint structure - Slows degeneration | - Mild to moderate osteoarthritis - Preventive care | Slow results (weeks/months) |
| Chondroitin | Mild-moderate cartilage wear | - Protects cartilage integrity - Reduces joint pain - Slows degradation | - Early/mid-stage osteoarthritis - Partial cartilage wear | Less effective for severe damage |
Combined Approach Many healthcare professionals recommend a combination of these supplements to maximize joint health benefits. For example, glucosamine and chondroitin are often taken together to provide comprehensive support for cartilage repair and protection. Adding hyaluronic acid can enhance joint lubrication and further reduce pain and inflammation.
Stanford Chemical Company (SCC) is an excellent supplier of sodium hyaluronate powder and various herbal extracts. We provide injectable-grade sodium hyaluronate powder, chondroitin, glucosamine, and other substances for relieving joint pain. For more information on these materials, please check our home page.
Conclusion
When it comes to choosing between hyaluronic acid, glucosamine, and chondroitin, there's no one-size-fits-all answer. Each supplement offers unique benefits that can address different aspects of arthrosis health. For immediate relief and improved lubrication, hyaluronic acid is a top choice. For long-term cartilage repair and maintenance, glucosamine is highly effective. The combination of glucosamine and chondroitin supports cartilage resilience and reduces inflammation.