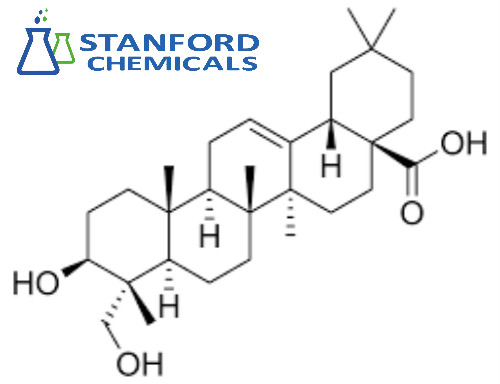
Hederagenin (CAS: 465-99-6) Description
Hederagenin (CAS: 465-99-6) is a naturally occurring triterpenoid found in plants such as English ivy. With a molecular formula of C30H48O4, this oleanane-type compound exhibits diverse pharmacological activities, including anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Its natural sources and unique chemical structure have made Hederagenin a subject of interest in pharmaceutical research, exploring its potential applications in drug development and therapeutic interventions. The compound's CAS number, 465-99-6, serves as a specific identifier in chemical databases.
Hederagenin (CAS: 465-99-6) Specifications
| Product Name |
Hederagenin |
| CAS Registry Number |
465-99-6 |
| Molecular Formula |
C30H48O4 |
| Molecular Weight |
472.710 g/mol |
| Assay |
≥97% |
| Solubility |
Methanol: 1 mg/mL |
Hederagenin (CAS: 465-99-6) Applications
Anti-tumor activity
Hederagenin has been shown to have a wide range of potential anti-tumor effects both in vitro and in vivo, which have been evaluated in various types of cancers, including lung, colon, stomach, liver, ovarian, prostate, breast, and endometrial cancers. The anti-tumor mechanisms of HG toward some tumors have been elucidated at the molecular level by gene or protein expression. In a study of the anti-hepatoma effect, HG decreased the tumor weight in H22 tumor-bearing mice, and increased the expression of P21, Bax, Fas, Fasl, caspase-3, and caspase-8 genes; Bax, Fas, Fasl, caspase-3, and caspase-8 mRNA; and Bax, Fasl, caspase-3, and caspase-8 proteins, whereas HG decreased the expression of mutant P53 and Bcl-2 genes; and Bcl-2 mRNA and Bcl-2 proteins.
Anti-inflammatory activity
As early as the 1970s, Hederagenin was found to show anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic activities in rats. In a mouse-ear edema model, where edema was induced by either croton oil or arachidonic acid, HG at a dose of 100 mg/kg showed anti-inflammatory activity with inhibition of 42% and 23%, respectively.
Anti-depressant activity
Previous studies have demonstrated that HG has an antidepressant effect by enhancing the signaling of central monoamines via inhibition of the reuptake of extracellular monoamines, including serotonin (5-HT), norepinephrine (NE), and dopamine (DA). In ex vivo and in vitro experiments, Hederagenin displayed affinity toward rat and cloned human monoamine transporters. However, HG showed no affinity toward a variety of other receptors from the central nervous system. In uptake assays using rat synaptosomes and transfected cells, HG was found to inhibit 5-HT, NE, and DA in a dose- and time-dependent manner, with a potency comparable to, or stronger than their corresponding specific inhibitors. Moreover, HG increased the extracellular concentrations of 5-HT, NE, and DA in the frontal cortexes of freely moving rats. Thus, HG was shown to be a new triple inhibitor of monoamine transporters.
Anti-neurodegenerative activity
HG-activated autophagy via the AMPK-mTOR and autophagy-related gene 7 (ATG 7) signaling pathways were able to accelerate the clearance of mutant huntingtin with 74 CAG repeats and A53Ta-synuclein and inhibit the oligomerization of a-synuclein in cellular models. A potential neuro-protective effect for Hederagenin in modulating Parkinson's and Huntington's diseases has been proposed based on its ability to facilitate the degradation of neurodegenerative disease proteins in cellular models and to improve the motor deficit of neurotoxin-injected mice. HG at concentrations of 3.13 and 6.25 mM was found to have a repairing action in the PC 12 cell injury model induced by Ab25-35. A high dose of 270 mg/kg improved the learning and memory ability of mice after cholinergic system damage induced by scopolamine, increased cerebral superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity, and reduced the TchE levels, which indicated that HG has potential for the treatment of senile dementia and brain nerve injury.
Anti-hyperlipidemia activity
0 In a Wistar rat atherosclerosis model, HG at a dose of 20 mg/kg reduced TC, TG, LDL-C, ALT, and AST levels and hemorheological parameters, and increased HDL-C levels and the high shear whole-blood viscosity index. The mechanism of action of Hederagenin may be related to the regulation of lipid metabolism, protection of liver function, improvement of blood rheology, and regulation of endothelial dysfunction.
Anti-leishmanial activity
Hederagenin is commonly used as a biopesticide. The leishmanicidal activity of the HG sodium salt was estimated in vitro on the promastigote and amastigote forms of two strains of Leishmania infantum isolated from dogs and a strain of Leishmania Tropica isolated from man. HG exhibited activity against the promastigote forms at concentrations of 50.54–202.14 mm, and activity against the amastigote forms was equivalent to that of the reference compound, N-methylglucamine antimonite.[1]
Reference
Jia Zeng, Ting Huang, Man Xue, Jianxing Chen, Linglin Feng, Ruofei Du, Yi Feng: Current knowledge and development of hederagenin as a promising medicinal agent: a comprehensive review. RSC Adv., 2018, 8, 24188
[1] Jia Zeng, Ting Huang, Man Xue, Jianxing Chen, Linglin Feng, Ruofei Du, Yi Feng: Current knowledge and development of hederagenin as a promising medicinal agent: a comprehensive review. RSC Adv., 2018, 8, 24188