Hyaluronic acid gel is a multi-functional product. It moisturizes, repairs, and soothes the skin.
1. What is Hyaluronic Acid Gel?
Hyaluronic acid gel is a gel-like product, like figure 1. Its key ingredient is hyaluronic acid (HA), which naturally found in our skin, joints, and eyes. HA can hold up to 1000 times its weight in water. Most hyaluronic acid gels available are not 100% pure HA. Instead, HA is the main active ingredient. It is mixed with water, thickeners (like carbomer), preservatives, and other beneficial ingredients. This creates a clear, lightweight gel that is easy to apply. It absorbs quickly and forms a breathable moisturizing layer on the skin. 
Fig 1. HA gel
2. How is Hyaluronic Acid Gel Made?
Making hyaluronic acid gel involves biotechnology and precise formulation. The process has two main steps: Step 1: Making the hyaluronic acid ingredient Today, most HA is made through microbial fermentation:
- Bacteria like Streptococcus equi are grown in large tanks. They are fed nutrients such as glucose. These bacteria produce and release hyaluronic acid.
- The HA is then separated and purified. Impurities like proteins and nucleic acids are removed.
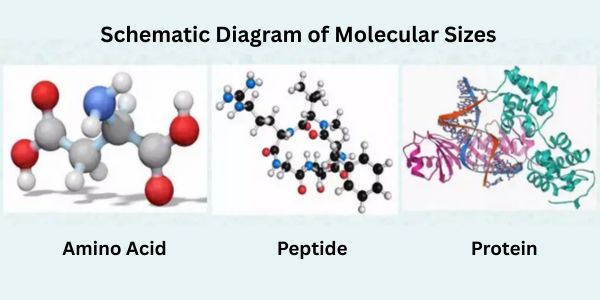
- The final product is dried and turned into a white powder—sodium hyaluronate. It can be processed into different molecular sizes:
- High molecular weight: form a film on the skin to lock in moisture.
- Medium molecular weight: provide moisture to the outer skin layers.
- Low molecular weight: penetrate deeper into the skin for better hydration.
Step 2: Making the gel Turning the powder into gel requires careful mixing:
- The powder is slowly added to purified water. It swells and forms a thick liquid.
- Thickeners like carbomer are added. The pH is adjusted to form a stable gel.
- Other ingredients are mixed in, such as moisturizers (e.g., glycerin), preservatives, and active compounds (e.g., vitamin B5 or centella extract).
Key factors for a good gel:
- Mixed molecular weights: better hydration at different skin levels.
- High purity: less likely to irritate, good for sensitive skin.
- Good formulation: affects stability, texture, and effectiveness.
* Stanford Chemicals Company (SCC) offers high-purity hyaluronic acid powder in various molecular weights. It is ideal for making hyaluronic acid gels.
3. Medical Uses of Hyaluronic Acid Gel
Hyaluronic acid gel is widely used in medical settings. For example, after orthopedic surgery, it can be applied to the treated area once nerves and tendons are repaired. It helps prevent tendon adhesions. Additionally, after abdominal surgery, medical-grade hyaluronic acid can be sprinkled into the abdominal cavity following irrigation. It effectively protects the intestinal surgical site and prevents adhesions that could lead to bowel obstruction. It is also commonly used in gynecology to prevent adhesions. Moreover, it can be used as an irrigation fluid during orthopedic surgeries. This helps reduce excessive inflammatory responses in the surgical area, minimizing scar formation. It may also serve other specific medical purposes.
4. Benefits of Hyaluronic Acid Gel for the Skin
Hyaluronic acid gel is a natural transparent polysaccharide. It was initially used mainly for moisturizing. Now, it is also used in wrinkle reduction and cosmetic procedures. It plumps the skin, smooths wrinkles, and enhances facial contours. HA gel naturally exists in a gel-like form in the dermis of human skin. It helps store water and increases skin volume. However, its levels decrease with age. This causes the skin to lose moisture, leading to dullness, aging, and wrinkle formation. Therefore, hyaluronic acid gel is primarily used in both medical and cosmetic fields.
5. Can Hyaluronic Acid Gel Remove Scars?
It does not significantly remove existing scars. Scars are a type of tissue that forms naturally as part of the skin’s healing process after injury. Applying hyaluronic acid gel has little effect on already formed scar tissue. Scars are a type of tissue that forms naturally as part of the skin’s healing process after injury. Applying hyaluronic acid gel has little effect on already formed scar tissue. But if the gel is applied just after skin damage occurs, it can reduce inflammation and support skin repair. HA is a high-molecular-weight polysaccharide. It is widely distributed throughout the human body, especially in the skin. It is a normal component of the dermis and belongs to the connective tissue. Therefore, HA gel has anti-inflammatory effects and can be absorbed directly by the skin.