Epigallocatechin Gallate Powder (EGCG) Description
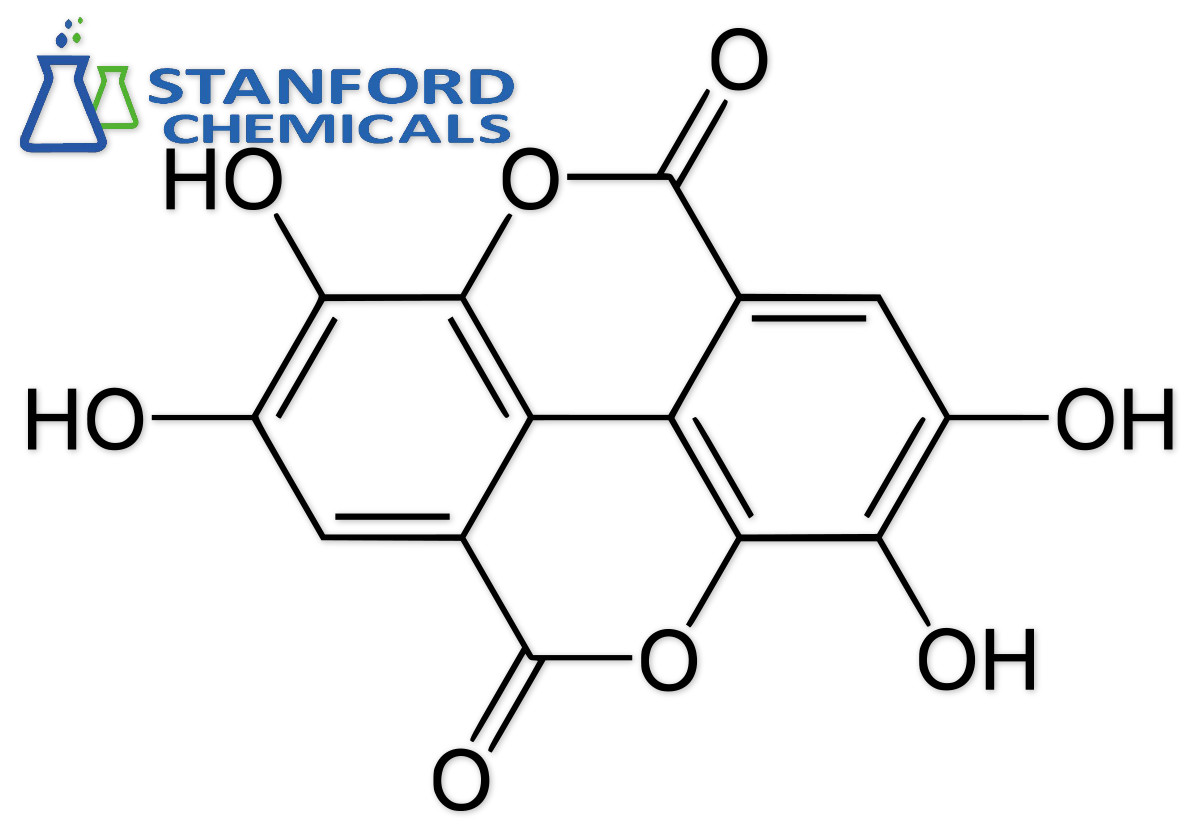
Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG) Powder is a fine, off-white to pale beige crystalline solid derived from green tea leaves. As the most abundant and bioactive catechin, it contains eight hydroxyl groups that confer exceptional antioxidant capacity. This polyphenol is water-insoluble but soluble in ethanol/alkaline solutions. It exhibits strong UV absorption (~273 nm) and demonstrates thermolability, degrading above 60°C. Its stability is pH-dependent, with optimal preservation in acidic conditions.
1. Chemical & Physical Properties
| Chemical Name |
Epigallocatechin Gallate |
| Molecular Formula |
C₂₂H₁₈O₁₁ |
| Appearance |
Off-white to pale beige crystalline powder |
| Organoleptic Properties |
Slightly bitter taste, minimal odor |
2. Structural Characteristics
- Molecular Structure: Gallocatechin backbone with eight hydroxyl groups
- Crystallography: Planar geometry facilitating π-π stacking interactions
- Spectroscopic Data:
- UV-Vis: Characteristic absorption maxima at 230 nm and 273 nm (conjugated ring systems)
- FTIR:
- 3200–3500 cm⁻¹ (hydroxyl stretch)
- 1690 cm⁻¹ (ester carbonyl)
- 1600 cm⁻¹ (aromatic C=C bonds)
- Physicochemical Parameters
| Property |
Value / Characteristics |
| Solubility |
Low in water; soluble in ethanol, methanol, DMSO, acetone |
| Thermal Stability |
Decomposition onset at ~60°C; significant degradation >100°C |
| Bulk Density |
~0.45 g/cm³ |
| Particle Size |
5–50 μm (typical distribution) |
- Stability & Storage
- Sensitivity: Oxygen-, light-, and temperature-sensitive
- Optimal Storage: -20°C under inert atmosphere (months-long stability)
- Degradation Pathways:
- Alkaline hydrolysis (pH-dependent)
- Oxidation (accelerated by heat/light)
- Epimerization & dimerization (at room temperature)
- Functional Properties
- Antioxidant Activity: pH-dependent, peaking in mildly acidic conditions
- Free Radical Scavenging: Enhanced by hydroxyl group arrangement
EGCG – Industrial & Biomedical Applications
1. Pharmaceuticals & Biomedicine
- Anticancer Therapy:
- Induces apoptosis via p53 activation
- Inhibits tumor angiogenesis (VEGF suppression)
- Nephroprotection: Attenuates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury via Wnt/β-catenin pathway modulation
- Antiviral Agent: Targets HIV-1 reverse transcriptase, HCV NS3 protease, and influenza neuraminidase
2. Food & Beverage Industry
- Emulsion Stabilizer: Inhibits oil droplet coalescence in starch-based gels (e.g., waxy maize)
- Antioxidant Delivery: Zein/chitosan nanoparticle encapsulation for sustained release in lipid-rich foods
3. Cosmetics & Personal Care
- Anti-Aging: Collagenase inhibition (reduces wrinkles)
- Skin Brightening: Tyrosinase suppression (melanin reduction)
- UV Protection: Acts as a natural photoprotectant
4. Materials Science
- Corrosion Resistance: Forms metal-polyphenol complexes on MgZnMn alloys for biomedical implants
- Polymer Crosslinking: Enhances biodegradability in food packaging & medical polymers
5. Agriculture & Veterinary Use
- Biopesticide: Controls Plasmopara viticola (grapevine downy mildew)
- Aquaculture Feed Additive: Boosts disease resistance in fish (e.g., trout)
6. Nutraceuticals & Supplements
- Weight Management: Modulates lipid metabolism
- Antioxidant Formulations: Encapsulated in tablets, capsules, and powders
7. Advanced Delivery Systems
- Mucoadhesive Nanocarriers: Nanocube sprays for oral submucous fibrosis treatment
- Transdermal Nanoparticles: Improves skin permeation & bioavailability
Epigallocatechin Gallate Powder (EGCG) FAQs
Q1. Is EGCG safe?
At typical supplemental doses (100–400 mg/day), EGCG is generally safe. High doses (>800 mg/day) may cause liver enzyme elevations in sensitive individuals. Contaminants like heavy metals can occur in low-purity products, so pharmaceutical-grade material is recommended. Avoid combining with hepatotoxic drugs.
Q2. How should it be stored?
Store EGCG powder airtight at –20°C under inert gas (e.g., nitrogen). Protect from light, moisture, and oxygen to prevent oxidation. Room-temperature storage accelerates degradation, turning the powder darker.
Q3. What distinguishes it from other catechins?
EGCG contains a gallate ester group absent in simpler catechins like EGC or EC, enhancing its antioxidant capacity 10–100-fold. This structure also enables unique interactions with cellular receptors and enzymes.