- Home
- Cosmetics & Personal Care
- Polyglutamic Acid (CAS No. 25513-46-6)
Polyglutamic Acid (CAS No. 25513-46-6)
| Catalog No. | |
| Synonym | PGA, L-Glutamic acid |
| CAS No. | 25513-46-6 |
| Content | ≥92% |
| Appearance | White crystalline powder |
Polyglutamic Acid is a synthetic polyamino acid having one COOH function per glutamic acid unit. Stanford Chemicals Company (SCC) offers high-quality Polyglutamic Acid with competitive pricing.
Related products: Hyafactor Polyglutamic Acid Sodium Polyglutamate Powder, Pure Cosmetic-Grade Hyaluronic Acid Powder Molecular Weight 200-600 KDa (HAC-N-SC)
- Description
Description
Polyglutamic Acid Description
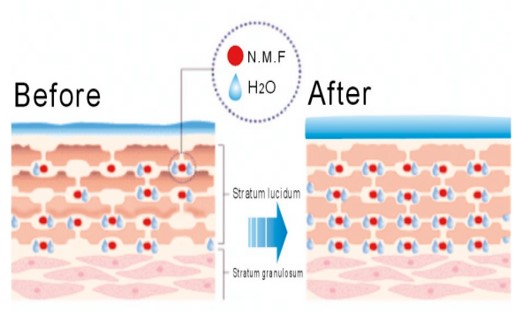
Polyglutamic Acid (PGA) is a natural biopolymer primarily produced through the fermentation of Bacillus subtilis. It consists of glutamic acid units connected by peptide bonds. Sodium polyglutamate dissolves easily in water and is a natural moisturizing agent. Its unique three-dimensional structure allows different molecular weights of sodium polyglutamate to work together, creating multiple layers of hydration. Because of these properties, it has become a widely used moisturizing ingredient in cosmetic products.
read more: Polyglutamic Acid: A “Better Alternative” to Hyaluronic Acid for Moisturizing Power
Polyglutamic Acid Specification
| Appearance | White crystalline powder or hydrogel |
| CAS No. | 25513-46-6 |
| Content | ≥92% |
| Loss on drying | ≤8% |
| Molecular Weight (Da) | ≥700000, 5 kDa to 2000 kDa |
| Heavy Metal Content (Pb) | ≤10mg/kg |
| Transmittance (5g/L, Solution, 400nm) | ≥95% |
| pH (10g/L, Solution, 25℃) | 5.0-7.5 |
| Total number of colonies | ≤100CFU/g |
Polyglutamic Acid Applications
- Cosmetics and Skincare: PGA is a highly effective moisturizer, known for retaining more water than hyaluronic acid, improving skin hydration, elasticity, and smoothness.
- Biomedical: Its biocompatibility and hydrogel-forming properties make it valuable in drug delivery, tissue engineering, and wound healing.
- Food Industry: PGA serves as a food additive for texture enhancement and water retention, commonly found in fermented products like natto.
- Agriculture: It is used in soil conditioners to enhance moisture retention for agricultural purposes.
The Advantages of Polyglutamic Acid Compared to Hyaluronic Acid
- Superior safety: Both the production strain of polyglutamic acid and polyglutamic acid itself are food-grade ingredients found on the dining table, with polyglutamic acid being one of the main components of natto. Its safety is beyond doubt.
- Exceptional hydration and moisturizing capabilities: The hydrating and moisturizing ability of polyglutamic acid is nearly 500 times that of hyaluronic acid.
- Low viscosity: Polyglutamic acid has low stickiness, with almost no adhesive feel. It feels light, thin, and smooth on the skin, is refreshing, easily absorbed, and provides a more pleasant skincare experience.
Polyglutamic Acid Packaging
Our Polyglutamic Acid is carefully handled during storage and transportation to preserve the quality of our product in its original condition.
500g/package, or customized.
FAQs
Q1: How is Polyglutamic Acid produced?
Polyglutamic Acid (PGA) is generally produced through the fermentation of Bacillus subtilis, yielding a high molecular weight polymer made of glutamic acid.
Q2: Is Polyglutamic Acid better than Hyaluronic Acid for hydration?
Both PGA and Hyaluronic Acid are excellent hydrators, but PGA can hold more water than Hyaluronic Acid. Additionally, PGA strengthens the skin barrier and helps prevent the breakdown of Hyaluronic Acid, making them effective when used together.
Q3: What forms of Polyglutamic Acid are available?
PGA comes in different molecular weights and formulations based on the application. In skincare, it’s often found in serums, creams, or gels. For biomedical and food uses, it may be available in powder or hydrogel forms. Custom products can be made with molecular weights ranging from 5 kDa to 2000 kDa, available as crystalline powder or hydrogel.