The molecular weight of hyaluronic acid (HA) varies widely, from low to high, giving it a range of physical and biological properties.
What is Hyaluronic Acid
Hyaluronic Acid (HA) is a polysaccharide naturally found in the connective tissues, skin, joint fluid, and eyes of the human body. It has a unique ability to retain water and is an important structural component in living organisms.
Benefits of Hyaluronic Acid
Due to its biocompatibility and versatility, HA is widely used in medicine, cosmetology, and bioengineering.
1. Joint Health
Hyaluronic acid plays a crucial role in joint health as a major component of synovial fluid, which lubricates and cushions the joints. It helps reduce friction between the joints, alleviating pain and improving mobility. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with osteoarthritis, as HA can help relieve symptoms and slow disease progression.
2. Ophthalmic Applications
In ophthalmology, hyaluronic acid is widely used in eye drops to relieve dry eye symptoms, providing long-lasting lubrication and comfort. During eye surgeries, HA is used to protect and repair corneal tissue, accelerate postoperative recovery, and reduce complications.
3. Tissue Repair and Regeneration
Hyaluronic acid promotes tissue repair and regeneration by stimulating cell proliferation and migration, speeding up the wound-healing process. It is beneficial in treating burns, ulcers, and other skin injuries, helping to reduce scar formation and enhance the quality of skin repair.
4. Anti-inflammatory and Immune Regulation
Hyaluronic acid exhibits significant anti-inflammatory and immune-regulating properties. It can reduce the release of inflammatory mediators, lowering inflammation and minimizing tissue damage. Additionally, HA can modulate the immune system, enhancing the body's defense mechanisms and helping to alleviate chronic inflammatory conditions.
5. Beauty and Skincare
In the field of beauty and skincare, hyaluronic acid is highly prized for its exceptional moisturizing capabilities. It can deeply hydrate the skin, increasing its water content, making it soft, and smooth, and reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. HA also promotes collagen production, enhancing skin elasticity and firmness, thus improving overall skin quality.
What is Molecular Weight
Molecular weight (MW), also known as relative molecular mass, is the sum of the masses of all the atoms in a molecule. It is used to measure the size of a molecule and is typically expressed in Daltons (Da) or atomic mass units (AMU). Calculating the MW of hyaluronic acid is complex because it is a high-molecular-weight polysaccharide made up of repeating disaccharide units (glucuronic acid and N-acetylglucosamine). The molecular weight depends on the chain length, i.e., the number of disaccharide units.
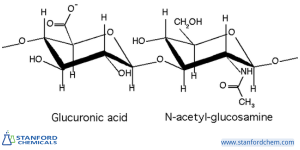
Fig 1. Hyaluronic acid chemical structure
In practice, the molecular weight of HA is usually expressed as a range. Low molecular weight HA is less than 200 kDa, medium molecular weight HA ranges from 200 to 1800 kDa, and high molecular weight HA is greater than 1800 kDa. These ranges represent the average number of disaccharide units in HA molecules, not precise single values.
How Molecular Weight Affects Hyaluronic Acid's Efficacy
The molecular weight of HA significantly influences its biological activity and efficacy.
1. Differences in Viscoelasticity and Lubricity
High molecular weight HA (typically over 1800 kDa) is widely used to treat arthritis due to its excellent viscoelastic and lubricating properties. It enhances the viscosity of joint fluid, reducing friction, pain, and inflammation. This type of HA is usually injected directly into the joint cavity for maximum effect.
On the other hand, Medium molecular weight HA (200-1800 kDa) is also used for joint health, often found in oral or injectable supplements. It provides lubrication and cushioning within the joint cavity, improving joint mobility and flexibility. In ophthalmic surgery, high molecular weight HA is commonly used, such as in cataract surgery and corneal transplants. Its high viscosity and viscoelasticity protect eye tissues, reducing mechanical damage during surgery. Conversely, low molecular weight HA (usually less than 200 kDa) is often used in eye drops. It effectively keeps the eyes moist, alleviating dry eye symptoms and improving eye comfort.
Fig 2. Low molecular weight hyaluronic acid eye drops
2. Different Effects on Wound Healing
Tissue Repair and Regeneration: In tissue engineering and regenerative medicine, high molecular weight HA is often used as a critical component of biomaterials and tissue engineering. Its structure can mimic the natural extracellular matrix, providing support and signals for cells, promoting cell migration, and tissue regeneration. Low molecular weight HA, due to its smaller molecular size, can better penetrate tissues, promoting wound healing and skin repair by activating fibroblasts and keratinocytes, accelerating the tissue regeneration process.
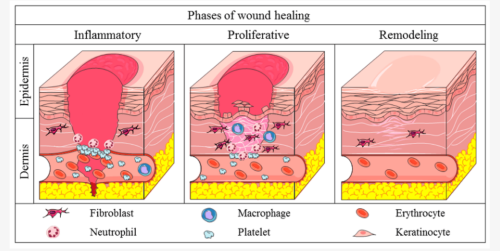
Fig 3. In the process of wound healing, different molecular weight hyaluronic acid has different effects
3. Variations in Anti-inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Effects
Anti-inflammatory and Immune Regulation: The role of HA in anti-inflammatory and immune regulation is also influenced by its molecular weight. Medium molecular weight HA shows certain advantages in anti-inflammatory and immune regulation. It can bind to cell surface receptors, regulating immune responses, and reducing inflammation, and is used to treat inflammatory diseases such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Low molecular weight HA has shown potential in some studies to regulate the immune system and promote antigen presentation, and immune responses, making it promising in vaccine development.
4. Varied Moisturizing Effects
Beauty and Skincare: In beauty and skincare, high molecular weight HA is mainly used for surface hydration in skincare products, forming a protective layer, reducing water loss, and enhancing skin smoothness. In contrast, low molecular weight HA can penetrate deeper into the skin, promoting hydration in the dermis layer, enhancing skin elasticity, and reducing fine lines and wrinkles, providing deeper skincare effects. 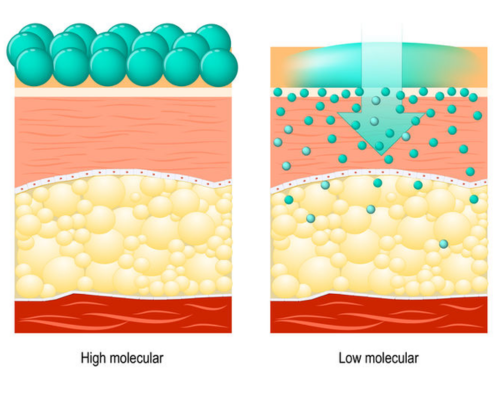
Fig 4. Varied Moisturizing Effects of High VS. Low Hyaluronic Acid
Conclusion
In summary, the molecular weight of HA significantly impacts its efficacy in different fields. High molecular weight HA is mainly used in applications requiring viscoelasticity and lubrication, such as joint health and ophthalmic surgery. In contrast, low molecular weight HA, due to its good permeability and biological activity, is more suitable for tissue repair, anti-inflammatory, immune regulation, and deep skin care. Choosing the appropriate molecular weight of HA can maximize its efficacy and meet the needs of different applications.
Stanford Chemical Company (SCC) is a pioneer in the development of hyaluronic acid. In addition to providing customers with food-grade, medical-grade, cosmetic-grade, and injectable-grade hyaluronic acid, we can also provide users with sodium hyaluronate powder with different molecular weights. For more information or specific applications, please visit our homepage.
Related reading: Comparative Analysis of Hyaluronic Acid with Different Molecular Weights High VS. Low Molecular Weight Hyaluronic Acid