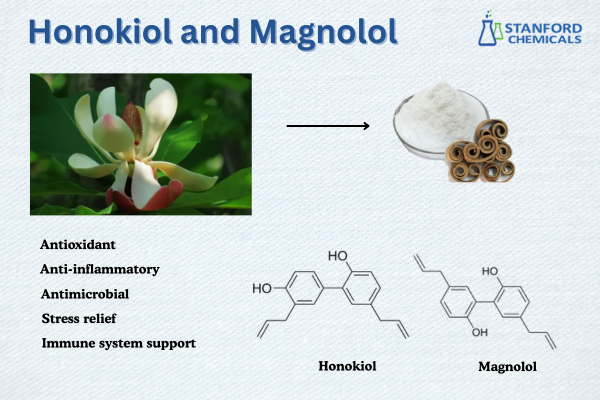
Honokiol and Magnolol are two other similar natural phenolic compounds extracted from the bark of the Magnolia tree. Despite being Isomers of each other, both products exhibit different pharmacological activities.
Honokiol: Benefits and Applications
Honokiol is one of the more prominent bioactive compounds isolated from the bark, seed cones, and leaves of the Magnolia tree, specifically the offgrand and the magnolia grandiflora. In terms of its chemistry, Honokiol is a type of biphenolic lignan because it has two phenol rings. Its structure is one of the factors contributing to the strong bioactivity exhibited by this compound. Another important aspect is its solubility. Honokiol is soluble in ethanol, methanol, and DMSO in moderate proportions but is not water-soluble. 
Health Benefits of Honokiol
Honokiol has been extensively investigated due to its various biological effects. It has most commonly been recognized for its potent antioxidant effects, thanks to which it has been found to offer protection to cells from oxidative damage. It also has notable anti-inflammatory effects, due to which it has been found to be beneficial for joint health. Moreover, the compound exhibits efficacy in inducing relaxation and modulating normal sleep patterns as a result of its activity as a GABA receptor modulator in the brain. Initial studies have also demonstrated potential application in the area of neurological health as a neuroprotective agent. In addition to that, it has also been found to possess anticancer properties.
Applications of Honokiol
Owing to its multifaceted advantages, honokiol is employed in a number of business types. In the nutraceutical industry, it is added to health supplements aimed at stress relief, improved sleep, and brain health. In the cosmetic industry, honokiol is prized for its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, making it an appropriate ingredient in anti-aging and skin soothing products. The pharmaceutical industry is studying its potential applications in the development of medications for neurological and inflammatory disorders.
Magnolol: Benefits and Applications
Another major active compound in Magnolia bark is Magnolol, which is commonly found along with Honokiol. Its structure is similar to that of Honokiol, being biphenolic. However, it differs slightly in terms of functional group arrangement. Similar to Honokiol, it is more soluble in organic solvents than in water.

Health Benefits of Magnolol
Magnolol is very well known for its potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. It also has potent antimicrobial and antifungal actions and thus can be very effective in either boosting the immune system or maintaining a healthy microbial balance. Magnolol has gained attention for its potential application and role in maintaining and supporting human metabolism, specifically within the regulation of lipids and cardiovascular function. There have also been findings suggesting that it can help support optimal cholesterol and healthy liver function. Moreover, magnolol can also support oral health through its antibacterial properties.
Applications of Magnolol
Magnolol is typically found in supplements that aid in boosting the immune system, preventing diseases associated with metabolism, and maintaining the health of the cardiovascular system. As an antimicrobial agent, magnolol is incorporated into various oral health supplements such as toothpaste and mouthwashes. In the cosmetic industry, magnolol is used as an antioxidant agent to combat aging skin.
Honokiol and Magnolol: Relationship and Differences
Honokiol and magnolol are both extracted from the bark of Magnolia species, which accounts for their many similarities. They are often extracted together.
Honokiol and Magnolol Similarities
- Chemical Properties: Both compounds are biphenolic. Their chemical structures are almost alike. Both compounds are poorly soluble in water. They are soluble in organic solvents.
- Health Uses: These two molecules demonstrate high antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties. They can be used to protect cells and the immune system and provide stress relief.
- Applications: Honokiol and magnolol are utilized in health supplements, cosmetics, and a few medications for similar uses, including stress relief, skincare, and the stimulation of the immune system.
- Applicability: Both are less water-soluble. This could be an area of concern when it comes to product development. Further clinical research has to be done to validate them.
Honokiol and Magnolol Synergistic Effects
When used in combination, the effects of honokiol and magnolol can complement each other. The combination usually results in a stronger antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effect than using each compound. The combination can be an essential ingredient in health supplements designed for comprehensive health support.
Key Differences between Honokiol and Magnolol
Despite their similarities, honokiol and magnolol exhibit distinct bioactivities. Honokiol is more frequently studied for its effects on the nervous system, such as promoting relaxation, improving sleep, and offering neuroprotection. Magnolol, on the other hand, is often highlighted for its antimicrobial, metabolic, and cardiovascular benefits. Their slight structural differences influence how they interact with biological targets and how they are metabolized in the body. Table 1. Key Differences between Honokiol and Magnolol
| Aspect | Honokiol | Magnolol |
| Chemical Structure | Two hydroxyl groups on different benzene rings | Two hydroxyl groups on the same benzene ring |
| Solubility | Slightly more soluble in organic solvents | Similar, sometimes less soluble than honokiol |
| Antioxidant | Strong activity | Strong activity |
| Anti-inflammatory | Effective, but usually less potent than magnolol | Especially strong; often used for anti-inflammation |
| Antimicrobial | Good effect | Strong effect, especially against certain bacteria/fungi |
| Neuroprotective | Well-documented; protects nerve cells, supports cognition | Limited, but some supportive evidence |
| Anxiolytic (Anti-anxiety) | Strong, widely studied; helps reduce anxiety and stress | Mild to moderate; less studied for this effect |
| Anticancer | Demonstrated in various cancer models, especially promising | Some effect, but less studied than honokiol |
| Metabolic Regulation | Some positive effects | More prominent; supports lipid and glucose metabolism |
| Pharmacokinetics | May have higher bioavailability in some forms | Different metabolic pathway; may be less bioavailable |
| Application Focus | Neurological, anticancer, stress relief | Anti-inflammatory, metabolic health, antimicrobial |
| Natural Abundance | Usually lower in Magnolia bark | Usually higher in Magnolia bark |
| Research Status | More studies on neuroprotection and anticancer | More studies on anti-inflammation and metabolism |
Separation and Purification
In industrial production, honokiol and magnolol can be separated and purified by using advanced chromatography, such as HPLC. As a result, a manufacturer can produce honokiol and magnolol of a desired purity or ratio, depending on the final use of these compounds. In this case, accurately separating honokiol and magnolol is crucial for maintaining consistent quality and effectiveness.
Conclusion
Honokiol and magnolol are two of the most important bioactive compounds derived from Magnolia bark. While they share many similarities, each offers unique benefits that make them valuable for a range of health and wellness applications. Whether used individually or in combination, these compounds provide significant opportunities for innovation in nutraceuticals, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. Stanford Chemicals Company offers over 1,300 herbal extract products, including Honokiol and Magnolol. If you require any of our products, please feel free to contact us for a quote.